Spring AOP 源码分析:创建代理(二)

Spring AOP 源码分析:入门 中,梳理出来了 Spring AOP 的入口。 Spring AOP 源码分析:获得通知 中着重介绍了如何获取通知。上一篇文章 Spring AOP 源码分析:创建代理(一) 重点介绍了一下切面链的组装和基于 JDK 动态代理的 AOP 的实现,这篇文章介绍一下基于 cglib 的代理类是生成。
cglib 简介

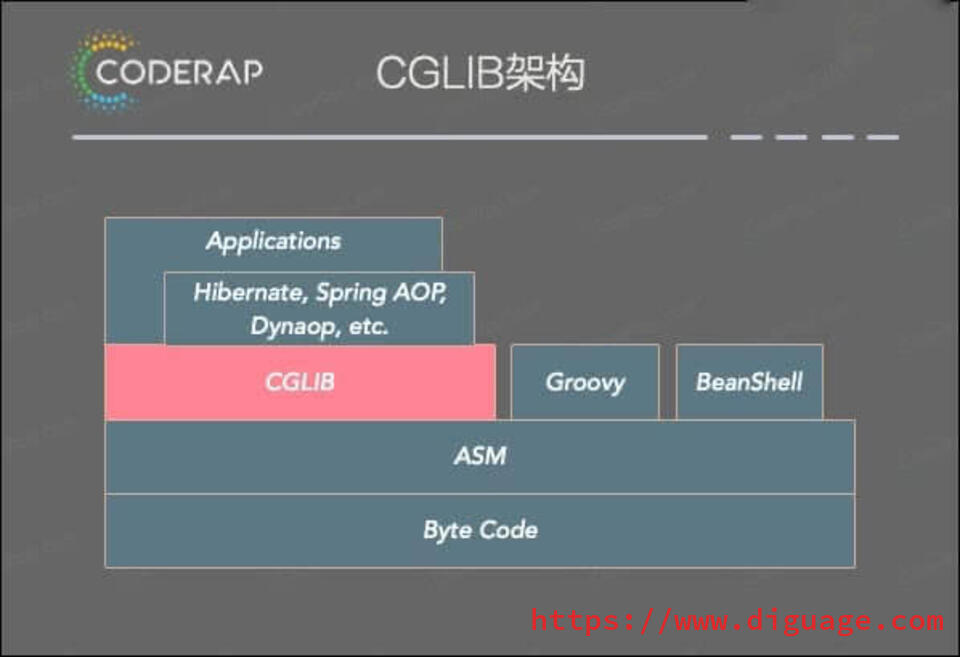
CGLIB(Code Generator Library)是一个高性能的代码生成库,被广泛应用于 AOP 框架(Spring)中以提供方法拦截功能,主要以继承目标类的方式来进行拦截实现,因此 CGLIB 可以对无接口的类进行代理。
CGLIB代理主要通过操作字节码的方式为对象引入方法调用时访问操作,底层使用了ASM来操作字节码生成新的类,ASM是一个短小精悍的字节码操作框架。CGLIB的应用栈如下:
JDK 动态代理是通过实现 InvocationHandler 接口,在其 invoke 方法中添加切面逻辑。而 cglib 则是通过实现 MethodInterceptor 接口,在其 invoke 方法中添加切面逻辑。
下面看一下在 Spring 中,是如何实现利用 cglib 来实现 AOP 编程的?
CglibAopProxy
先看一下创建代理对象的方法:
CglibAopProxy#getProxy(ClassLoader)@Override
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating CGLIB proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
try {
Class<?> rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();
Assert.state(rootClass != null, "Target class must be available for creating a CGLIB proxy");
Class<?> proxySuperClass = rootClass;
if (rootClass.getName().contains(ClassUtils.CGLIB_CLASS_SEPARATOR)) {
proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass();
Class<?>[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> additionalInterface : additionalInterfaces) {
this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface);
}
}
// Validate the class, writing log messages as necessary.
// 验证 Class
validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader);
// Configure CGLIB Enhancer...
Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer();
if (classLoader != null) {
enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader);
if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader &&
((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) {
enhancer.setUseCache(false);
}
}
enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);
enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));
enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);
enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareGeneratorStrategy(classLoader));
// 设置拦截器
Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass);
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length];
for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) {
types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass();
}
// fixedInterceptorMap only populated at this point, after getCallbacks call above
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter(
this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset));
enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);
// Generate the proxy class and create a proxy instance.
// 生成代理类以及创建代理
return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks);
}
catch (CodeGenerationException | IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of " + this.advised.getTargetClass() +
": Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",
ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// TargetSource.getTarget() failed
throw new AopConfigException("Unexpected AOP exception", ex);
}
}这里的关键是创建 Callback 数组,这里封装着切面逻辑。
CglibAopProxy#getCallbacksprivate Callback[] getCallbacks(Class<?> rootClass) throws Exception {
// Parameters used for optimization choices...
// 对 expose-proxy 属性的处理
boolean exposeProxy = this.advised.isExposeProxy();
boolean isFrozen = this.advised.isFrozen();
boolean isStatic = this.advised.getTargetSource().isStatic();
// Choose an "aop" interceptor (used for AOP calls).
// 将拦截器封装在 DynamicAdvisedInterceptor 中
Callback aopInterceptor = new DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(this.advised);
// Choose a "straight to target" interceptor. (used for calls that are
// unadvised but can return this). May be required to expose the proxy.
Callback targetInterceptor;
if (exposeProxy) {
targetInterceptor = (isStatic ?
new StaticUnadvisedExposedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) :
new DynamicUnadvisedExposedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource()));
}
else {
targetInterceptor = (isStatic ?
new StaticUnadvisedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) :
new DynamicUnadvisedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource()));
}
// Choose a "direct to target" dispatcher (used for
// unadvised calls to static targets that cannot return this).
Callback targetDispatcher = (isStatic ?
new StaticDispatcher(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) : new SerializableNoOp());
Callback[] mainCallbacks = new Callback[] {
// 将拦截器链加入 Callback 中
aopInterceptor, // for normal advice
targetInterceptor, // invoke target without considering advice, if optimized
new SerializableNoOp(), // no override for methods mapped to this
targetDispatcher, this.advisedDispatcher,
new EqualsInterceptor(this.advised),
new HashCodeInterceptor(this.advised)
};
Callback[] callbacks;
// If the target is a static one and the advice chain is frozen,
// then we can make some optimizations by sending the AOP calls
// direct to the target using the fixed chain for that method.
if (isStatic && isFrozen) {
Method[] methods = rootClass.getMethods();
Callback[] fixedCallbacks = new Callback[methods.length];
this.fixedInterceptorMap = new HashMap<>(methods.length);
// TODO: small memory optimization here (can skip creation for methods with no advice)
for (int x = 0; x < methods.length; x++) {
Method method = methods[x];
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, rootClass);
fixedCallbacks[x] = new FixedChainStaticTargetInterceptor(
chain, this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget(), this.advised.getTargetClass());
this.fixedInterceptorMap.put(method, x);
}
// Now copy both the callbacks from mainCallbacks
// and fixedCallbacks into the callbacks array.
callbacks = new Callback[mainCallbacks.length + fixedCallbacks.length];
System.arraycopy(mainCallbacks, 0, callbacks, 0, mainCallbacks.length);
System.arraycopy(fixedCallbacks, 0, callbacks, mainCallbacks.length, fixedCallbacks.length);
this.fixedInterceptorOffset = mainCallbacks.length;
}
else {
callbacks = mainCallbacks;
}
return callbacks;
}CGLIB 是通过 MethodInterceptor 来实现方法的拦截和增强的。所以,CglibAopProxy 实现的 AOP 的增强都被封装在了 CglibAopProxy.DynamicAdvisedInterceptor 类的 intercept 中。
CglibAopProxy.DynamicAdvisedInterceptorprivate static class DynamicAdvisedInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable {
private final AdvisedSupport advised;
public DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(AdvisedSupport advised) {
this.advised = advised;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
Object target = null;
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.getTargetSource();
try {
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
// Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target, in case it comes from a pool...
target = targetSource.getTarget();
Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null);
// 获取拦截器链
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
Object retVal;
// Check whether we only have one InvokerInterceptor: that is,
// no real advice, but just reflective invocation of the target.
if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly.
// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor, so we know
// it does nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot
// swapping or fancy proxying.
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
// 如果拦截器链为空则直接激活原方法
retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse);
}
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
// 进入链
retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
}
retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal);
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
// 省去 equals 和 hashCode 方法
}还是熟悉的配方,还是熟悉的味道,又看到了 this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass) 了。
无论是 JdkDynamicAopProxy,还是 CglibAopProxy,它们也只是做了基本处理,而真正对 Advice(通知/增强) 的链式调用都是通过 AdvisedSupport#getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice 最终委托给了 DefaultAdvisorChainFactory#getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice 方法来生成 Advice(通知/增强)链,然后通过 ReflectiveMethodInvocation 及其子类来调用到 Advice(通知/增强)链。
在 JdkDynamicAopProxy 的 invoke 方法中,通过创建 ReflectiveMethodInvocation 对象,调用其 proceed() 方法,来完成增强的链式调用。
在 CglibAopProxy 的 intercept 方法中,通过创建 CglibMethodInvocation 对象,调用其 proceed() 方法,来完成增强的链式调用。 CglibMethodInvocation 继承了 ReflectiveMethodInvocation。其实, CglibMethodInvocation 也是通过调用父类方法完成 AOP 切面调用的。这里就不再贴代码赘述了。
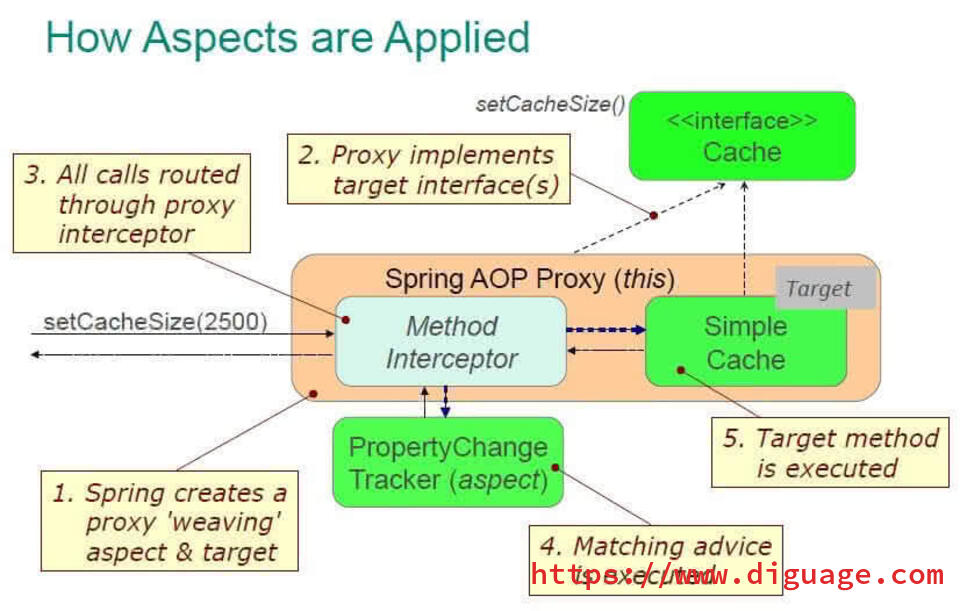
总结
最后,使用前面文章提到的“Aspect 应用流程”再来总结一下 Spring AOP 的调用过程: